Deep Cycle Battery Life: Comparing Durability of LiFePO4 and Lithium Ion vs Lead-Acid
As someone who relies on deep cycle batteries for power for myself and my customers, it's important to understand the differences between lithium iron phosphate (LiFePO4), lithium ion and lead-acid batteries when it comes to durability and battery life. While both types of batteries have their advantages and disadvantages, it's important to choose the one that best suits your needs. This article will discuss deep cycle battery life comparing LiFePO4, lithium ion vs lead-acid durability.

LiFePO4 batteries have a longer cycle life than lead-acid batteries, meaning they can be charged and discharged more times before they start to lose capacity. In addition, LiFePO4 batteries are generally lighter and have a higher energy-to-weight ratio than lead-acid batteries. However, LiFePO4 batteries are typically more expensive than lead-acid batteries.
On the other hand, lead-acid batteries are cheaper and have been around for much longer than LiFePO4 batteries. They are also widely available and can be found in many different sizes and capacities. However, lead-acid batteries have a shorter lifespan than LiFePO4 batteries and can be permanently damaged if they are deeply discharged.
Key Takeaways
- Understanding the differences between LiFePO4 and lead-acid batteries is important when it comes to durability and battery life.
- LiFePO4 batteries have a longer cycle life and are generally lighter than lead-acid batteries, but they are also more expensive.
- Lead-acid batteries are cheaper and widely available, but have a shorter lifespan and can be damaged if deeply discharged.
Deep Cycle Battery Life
When it comes to deep cycle batteries, lifespan is a crucial factor to consider. The two most popular types of deep cycle batteries are Lithium Iron Phosphate (LiFePO4) and Lithium Ion (Li-ion) batteries, and they both have a significantly longer lifespan than traditional lead-acid batteries.
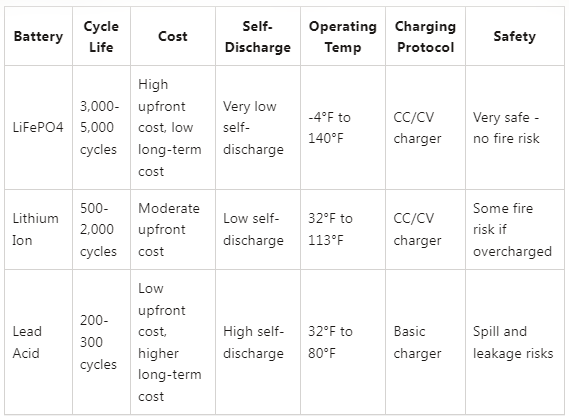
LiFePO4 batteries are known for their impressive cycle life, which can range from 3,000 to 5,000 cycles or more. This means that they can be discharged and recharged more times than a typical Li-ion or lead-acid battery. Additionally, LiFePO4 batteries can reach a 100% depth of discharge (DOD), which means they can be drained completely without causing any damage to the battery.
Li-ion batteries, on the other hand, have a slightly shorter cycle life than LiFePO4 batteries, typically ranging from 500 to 2,000 cycles. However, they still offer a longer lifespan than lead-acid batteries, and they have a higher energy density, which means they can store more energy in a smaller space.
When it comes to durability, LiFePO4 batteries are the clear winner. They are known for their excellent thermal stability and safety, and they can operate in a wider range of temperatures without any degradation in performance. In contrast, Li-ion batteries have a more limited temperature range and can be more prone to thermal runaway, which can cause safety issues.
Overall, both LiFePO4 and Li-ion batteries offer significant advantages over lead-acid batteries in terms of lifespan and durability. However, LiFePO4 batteries are the better choice for applications that require a longer cycle life and enhanced safety, while Li-ion batteries are a good choice for applications that require a higher energy density.
Lithium Iron Phosphate (LiFePO4) vs Lead-Acid Durability
Understanding LiFePO4 Durability
LiFePO4 batteries are known for their superior durability compared to lead-acid batteries. They can last up to 10 years or 5,000+ cycles, depending on usage. This is due to their ability to withstand high charge and discharge rates without significant capacity loss. Additionally, they have a high energy density, which means they can store a large amount of energy in a small size and weight.
Another factor that contributes to the durability of LiFePO4 batteries is their ability to operate at a wide range of temperatures. They can function well in extreme temperatures, from -20°C to 60°C, without any significant impact on their performance. This makes them ideal for use in off-grid systems, where the temperature can fluctuate significantly.
Decoding Lead-Acid Durability
Lead-acid batteries, on the other hand, have a shorter lifespan compared to LiFePO4 batteries. A premium deep cycle lead-acid battery typically lasts 3-5 years or 600-1,000 cycles, whereas an inexpensive deep cycle lead-acid battery generally lasts 2-3 years or 200-300 cycles.
One of the main factors that affect the durability of lead-acid batteries is the temperature. The cycle life of a lead-acid battery is reduced by half for every 15ºF above 75ºF. This means that if the battery operates at a temperature of 90ºF, its cycle life will be reduced by half.
Another factor that affects the durability of lead-acid batteries is their sensitivity to overcharging and deep discharging. Overcharging can cause the battery to generate excess heat, which can damage the plates and cause the battery to fail prematurely. Similarly, deep discharging can cause sulfation, which can also reduce the battery's lifespan.
Overall, LiFePO4 batteries are more durable compared to lead-acid batteries. They have a longer lifespan, can operate at a wide range of temperatures, and are less sensitive to overcharging and deep discharging.
Lithium Ion Battery Life
The Lifespan of Lithium Ion Batteries
Lithium ion batteries have a longer lifespan than traditional lead-acid batteries. They typically last around 2-3 years, depending on the usage and charging habits. However, with proper care and maintenance, lithium ion batteries can last up to 10 years in the right conditions.
Factors Affecting Lithium Ion Battery Life
Several factors can affect the lifespan of lithium ion batteries. These include:
- Temperature: High temperatures can reduce the lifespan of lithium ion batteries. It is recommended to keep the batteries at room temperature or below.
- Depth of Discharge: The more deeply a lithium ion battery is discharged, the shorter its lifespan. It is recommended to avoid discharging the battery below 20%.
- Charging Habits: Overcharging or undercharging a lithium ion battery can reduce its lifespan. It is recommended to use a charger specifically designed for lithium ion batteries and to avoid leaving the battery on the charger for extended periods.
- Quality: The quality of the lithium ion battery can also affect its lifespan. It is recommended to purchase batteries from reputable manufacturers.
Overall, lithium ion batteries offer a longer lifespan and better performance than traditional lead-acid batteries. By following proper care and maintenance guidelines, lithium ion batteries can last up to 10 years, making them a cost-effective and reliable option for deep cycle applications.
Roundup of Deep Cycle Battery Life
When it comes to deep cycle battery life, lithium iron phosphate (LiFePO4) and lithium ion batteries last much longer than lead acid batteries. But each has pros and cons.
Lifespan Comparison
- LiFePO4 batteries: 3,000-5,000 cycles
- Lithium ion batteries: 500-2,000 cycles
- Lead acid batteries: 200-300 cycles
LiFePO4 batteries have the longest lifespan, retaining 80% capacity for over 3,000 cycles. High quality lithium ion batteries can last up to 2,000 cycles. But standard lead acid batteries last only 200-300 cycles before capacity drops significantly.
Cost Differences
While LiFePO4 batteries have a higher upfront cost, their long lifespan results in a lower total cost of ownership over time compared to lead acid batteries. Lithium ion batteries fall somewhere in between on upfront cost.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the lifespan of a LiFePO4 battery?
LiFePO4 batteries have a longer lifespan than lead-acid batteries. They can last up to 10 times longer than lead-acid batteries, depending on the specific application. Typically, they are rated to deliver 3,500 cycles at 100% depth of discharge (DOD).
What are the advantages of LiFePO4 over lead-acid batteries?
LiFePO4 batteries have several advantages over lead-acid batteries. They have a longer lifespan, are more durable, and can handle more charge and discharge cycles. They are also more environmentally friendly, as they do not contain toxic chemicals.
How does the cycle life of LiFePO4 compare to lithium-ion batteries?
LiFePO4 batteries have a longer cycle life than lithium-ion batteries. They can last up to 10 times longer than lead-acid batteries, while lithium-ion batteries typically last for around 500-2000 cycles.
Are LiFePO4 batteries more durable than lead-acid batteries?
Yes, LiFePO4 batteries are more durable than lead-acid batteries. They can handle more charge and discharge cycles, and are less prone to damage from overcharging or discharging. They are also more resistant to temperature changes and can operate in a wider range of temperatures.
What is the expected lifespan of a lithium-ion battery?
The expected lifespan of a lithium-ion battery depends on the specific application and usage. Generally, they last for around 500-2000 cycles, or 2-3 years with regular use.
What are the safety advantages of using lithium-ion batteries over lead-acid batteries?
Lithium-ion batteries are safer than lead-acid batteries. They are less prone to thermal runaway and overheating, which can lead to battery fires. They also do not contain toxic chemicals, making them more environmentally friendly.
What are some charging tips for batteries?
Charging for Maximum Battery Life
To maximize cycle life, follow the charging guidelines for each battery type:
- LiFePO4 - Use a constant current, constant voltage (CC/CV) lithium battery charger. Avoid overcharging.
- Lithium Ion - Use a CC/CV lithium ion battery charger. Don't discharge below 20% or overcharge.
- Lead Acid - Prevent deep discharging. Recharge fully then stop. Equalize charge every 10-20 cycles.
What are safety and environmental factors to consider with batteries?
Lithium batteries offer safety advantages over lead acid:
- No risk of dangerous acid leaks or fumes
- Less risk of fire or explosion
However, lithium batteries require proper disposal and recycling. Lead acid batteries are very recyclable.
