How Much Gas Does a Generator Use: A Comprehensive Guide
When it comes to generator fuel consumption, there are several factors to consider.
The type of fuel used, the generator’s capacity, and the load it’s running at all play a role in determining how much fuel a generator will consume.
Fuel consumption is typically measured in gallons per hour (GPH) or cubic feet per hour (CFH) and varies depending on the type of fuel used.
Gasoline generators typically use between 0.6 and 1 gallon of fuel per hour, while propane generators use about 0.4 gallons per hour, and diesel generators use around 0.88 gallons per hour [1].
The generator’s capacity and load also impact fuel consumption.
The higher the capacity, the more fuel the generator will consume. Similarly, the higher the load, the more fuel the generator will consume.
It’s important to note that running a generator at full capacity for an extended period of time will result in higher fuel consumption than running it at a lower load.
Fuel efficiency is an important factor to consider when choosing a generator.
Energy-efficient appliances and electronics can help reduce the overall electricity consumption and, in turn, the fuel consumption of the generator.
It’s also important to consider the wattage requirements of the appliances and electronics you plan to power with the generator.
Fuel costs can add up quickly, so it’s important to factor in the cost to run the generator when making a purchasing decision.
Gasoline generators can cost around $52 per day to operate, propane generators can cost over $200 per day, and natural gas generators typically range from $20 to $40 per day [1].
Types of Generators and Fuel Usage
When it comes to generators, there are several types available on the market. Each type has its own unique features and fuel usage. In this section, we will discuss the most common types of generators and their fuel usage.
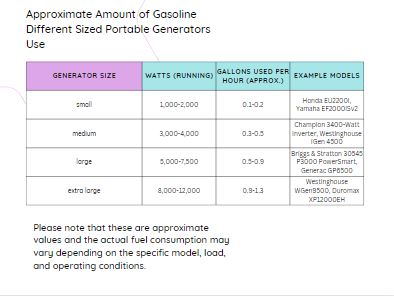
Portable Generators
Portable generators are small, compact, and easy to move around. They are ideal for outdoor activities, camping trips, and small power needs.
Portable generators come in both gasoline and propane fuel types. Gasoline generators are more common and typically consume between 0.6 and 1 gallon of fuel per hour. Propane generators, on the other hand, use about 0.4 gallons per hour.
The specific amount of gas a generator uses can depend on the generator’s size, power output, and load.
Standby Generators
Standby generators are larger and designed to be permanently installed outside the home or business. They are connected to the home’s electrical system and automatically turn on when there is a power outage.
Standby generators are available in both natural gas and propane fuel types. Natural gas generators typically range from $20 to $40 per day, while propane generators can cost over $200 per day.
Inverter Generators
Inverter generators are a newer type of generator that uses advanced technology to produce cleaner and more efficient power.
They are typically smaller and lighter than traditional generators, making them ideal for camping and outdoor activities.
Inverter generators are available in both gasoline and propane fuel types. Gasoline generators consume between 0.6 and 1 gallon of fuel per hour, while propane generators use about 0.4 gallons per hour.
Dual Fuel Generators
Dual fuel generators are designed to run on two different types of fuel, typically gasoline and propane.
They are ideal for those who want the flexibility to switch between fuel types depending on availability and cost.
Dual fuel generators typically consume between 0.6 and 1 gallon of gasoline per hour and about 0.4 gallons of propane per hour.
Tri-Fuel Generators
Tri-fuel generators are similar to dual fuel generators but can run on three different types of fuel: gasoline, propane, and natural gas.
They are ideal for those who want the ultimate flexibility in fuel options.
Tri-fuel generators typically consume between 0.6 and 1 gallon of gasoline per hour, 0.4 gallons of propane per hour, and 210 cubic feet of natural gas per hour.
Generator Sizing and Load Considerations
When it comes to generator sizing, it is essential to consider the size of the generator, the wattage requirements of your appliances, and the load percentage.
The generator size is typically measured in kilowatts (kW), and the wattage requirements of your appliances vary depending on the type of appliance you have.
One of the essential factors to consider when sizing a generator is the load percentage.
This percentage refers to the amount of power being used by your appliances at any given time. It is crucial to size your generator correctly to ensure that it can handle the load percentage of your appliances.
For example, if you have a 5000-watt refrigerator, a 1500-watt coffee maker, a 1200-watt microwave, a 700-watt freezer, a 4500-watt water heater, and a 3000-watt stovetop, the total wattage requirement would be 16,400 watts.
To calculate the load percentage, you would divide the total wattage requirement by the generator’s rated output.
For instance, if you have a 20 kW generator, the load percentage would be 82%. This means that the generator is operating at 82% of its rated output.
It is also essential to consider the starting wattage of your appliances.
Some appliances, such as refrigerators and freezers, require more power to start than they do to run. It is crucial to factor in the starting wattage when sizing your generator to ensure that it can handle the initial surge of power.
Operational Costs and Efficiency
When using a generator, the operational cost and efficiency are two of the most important factors to consider.
Knowing how much gas your generator uses can help you determine the cost to run it and plan your budget accordingly.
The fuel costs for running a generator can vary depending on the type of fuel used.
Gasoline generators typically use between 0.6 and 1 gallon of fuel per hour, while propane generators use about 0.4 gallons per hour. Natural gas generators are the most cost-effective, with a range of $20 to $40 per day.
To save on fuel costs, you can consider investing in a generator with higher efficiency.
Diesel generators are generally more fuel-efficient than gas generators due to the higher energy density of diesel fuel. This allows diesel generators to run more efficiently and for longer periods on the same amount of fuel.
Generator efficiency is also an important factor to consider.
The efficiency of a generator determines how much energy is produced per unit of fuel consumed. A higher efficiency generator will produce more energy while using less fuel.
To improve the fuel efficiency of your generator, you can take steps such as regular maintenance, proper storage, and keeping the generator in a well-ventilated area.
These steps can help ensure that your generator is running at its optimal level and using fuel efficiently.
Maintenance and Performance
To ensure that your generator runs efficiently and uses the least amount of gas possible, regular maintenance is crucial. Here are some maintenance tips to keep your generator in top shape:
- Change the oil and air filter regularly according to the manufacturer’s instructions. Dirty oil and air filters can cause the generator to work harder, which can increase gas consumption.
- Check the spark plug and replace it if necessary. A dirty or damaged spark plug can cause the generator to use more gas than necessary.
- Keep the fuel tank clean and free of debris. Debris in the fuel tank can clog the fuel line and cause the generator to work harder, which can increase gas consumption.
- Use high-quality fuel. Using low-quality fuel can cause the generator to work harder, which can increase gas consumption.
- Store your generator properly. When not in use, store your generator in a dry, clean place. Exposure to weather conditions such as humidity or cold weather can cause damage to the generator and increase gas consumption.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the fuel consumption rate for generators per hour?
The fuel consumption rate for generators varies depending on the wattage and type of fuel used. According to Power Equip Hub, gasoline generators typically use between 0.6 and 1 gallon of fuel per hour, while propane generators use about 0.4 gallons per hour. Natural gas generators typically range from $20 to $40 per day.
How long can a generator run on a full tank of gas?
The length of time a generator can run on a full tank of gas depends on the generator’s fuel efficiency and the size of its fuel tank.
On average, a 5000-watt generator can run for about 8 hours on a full tank of gas, while a 10000-watt generator can run for up to 12 hours on a full tank of gas. However, this can vary depending on the generator’s fuel consumption rate and the load it’s powering.
What is the difference in fuel usage between a 5000 watt and a 10000 watt generator?
The fuel usage of a 5000-watt generator and a 10000-watt generator varies significantly. A 5000-watt generator typically uses about 0.75 gallons of gas per hour. Meanwhile, a 10000-watt generator can use up to 1.5 gallons of gas per hour. This means that a 10000-watt generator will consume twice as much fuel as a 5000-watt generator.
How does a dual fuel generator’s gas consumption compare to a standard one?
Dual fuel generators are designed to run on both gasoline and propane, which can help to reduce fuel costs and increase runtime. According to Generator Advice, a dual fuel generator’s gas consumption is typically lower than that of a standard gasoline generator. However, the exact fuel consumption rate will depend on the generator’s wattage, fuel efficiency, and the type of fuel it’s running on.
Can you estimate the daily gasoline consumption of an average generator?
The daily gasoline consumption of an average generator will depend on several factors, including the generator’s wattage, fuel efficiency, and the load it’s powering. On average, a 5000-watt generator will consume about 3.75 gallons of gas per day if it’s running at full capacity for 5 hours. However, this can vary significantly depending on the generator’s fuel consumption rate and the load it’s powering.
What factors influence the fuel efficiency of a portable generator?
The fuel efficiency of a portable generator can be influenced by several factors. These include the generator’s engine type, size, and load capacity. Additionally, the type of fuel used can also affect the generator’s fuel efficiency.
For example, propane is generally more efficient than gasoline, while natural gas is the most efficient fuel for generators. Proper maintenance and regular servicing can also help to improve a generator’s fuel efficiency.

